Your cart is currently empty!
Category: Anti Inflammation
-

An Inflammatory Lifestyle May Put You at Risk
Your greatest health risk is chronic inflammatory-related diseases, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). In fact, they say it is the most significant health risk to all humanity worldwide!
Here is the good yet tragic news! Chronic disease is largely preventable, but most just accept this very harmful robber of health and eventually wealth. An article published by World Health Organization states, “Although more basic research may be needed on some aspects of the mechanisms that link diet to health, the currently available scientific evidence provides a sufficiently strong and plausible basis to justify taking action now. Beyond the appropriate medical treatment for those already affected, the public health approach of primary prevention is considered to be the most cost-effective, affordable and sustainable course of action to cope with the chronic disease epidemic worldwide.”
I encourage you to not accept these modifiable diseases as age-related issues that you have no course of action against. You do! You can make the choices to support your body systems and organs that promote wellness. Your body is designed to keep you well. We have bought into the idea of medication and disease management as the way to greater wellness. Yes, thankfully, we have modern medicine. But we also have modern processed foods, sedentary lifestyles perpetuated by devices like television, computers, cell phones, etc., that engage us as we sit and further encouraging chronic inflammation from the lack of physical activity. Dr. Thomas Frieden, the former Director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), says the closest thing to a wonder drug is walking! Yes, one of the Ten Essentials of Wellness. He is quoted in Harvard Medical School material as stating, “Walking can have a bigger impact on disease risk and various health conditions than just about any other remedy that is available to you.”

National Institutes of Health identifies risks you should be aware of in understanding and identifying chronic inflammation your number one health risk.
- Age: Age is measured by free radical accumulation, not years and other related factors like increase in visceral body fat.
- Diet: A diet rich in saturated fats, trans-fats and refined sugar is associated with higher production of pro-inflammatory molecules.
- Obesity: Some reports show that body mass index of an individual is proportional to the pro-inflammatory cytokines secreted.
- Low Sex Hormones: Maintaining levels of sex hormone, like testosterone and estrogen, reduce the risk of inflammatory diseases.
- Stress and Sleep disorders: Both physical and emotional stress is associated with the inflammatory cytokine release. Furthermore, sleep disorders are considered an independent risk factor for chronic inflammation.
I have to go on and give you indications of the symptoms related to chronic inflammation in the NIH article. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Body pain
- Constant fatigue and insomnia
- Depression, anxiety, and mood disorders
- Gastrointestinal complications like constipation, diarrhea, and acid reflux.
- Weight gain
- Frequent infections
Say no to chronic inflammation. Say no to foods that promote inflammation like refined carbs, fried foods, sugar-sweetened soda, processed meats, margarine, shortening and lard. And say yes to physical activity as one of the most important anti-inflammatory activities. You don’t have to be in the gym. Walking is next to being the closest things to a wonder drug, and it can be done anywhere!
I invite you to listen to my podcast<link> with Jarir Nakouzi, M.D. as he sheds great insights into chronic inflammation. He is a renowned international lecturer, and I think you will find it very informative.
As National Institutes of Health relates, chronic inflammation is not a specific disease, it is a mechanistic process of the immune system, that if left uncheck and uncontrolled, can lead to many harmful effects. The good news, you can do so much to impact your health and have healthy inflammation responses.
Blessings of wellness to you!
-

Reduce Inflammation with These Four Low-Impact Exercises
Chronic inflammation can be debilitating. It can make you feel tired, lead to aches and pains, reduce your mobility and joy for life. But studies are showing that a surprisingly small amount of daily exercise can help reduce your inflammation
. A study published in Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, showed that just 20 minutes of brisk walking could produce anti-inflammatory effects. During exercise or physical exertion, the brain and sympathetic nervous system are activated. Hormones are then released into the blood and trigger immune cell responses which help boost the immune system and reduce inflammation
. While the study focused strictly on brisk walking, there are other ways to exercise that support healthy inflammation levels. Here are four low-impact exercises to try.
Swimming

Swimming has numerous benefits, from increasing flexibility, improving muscle mass and strength, and improving cardiovascular and lung health. Swimming also allows you to choose your intensity and is low-impact, which makes it an excellent exercise for anyone.
Walking
Walking is the ultimate form of exercise because it is free, requires no special equipment and can be done anywhere! Keep in mind that if you are new to exercise or have any physical limitations, speak with your doctor and go at your own pace.
Yoga
Yoga, especially when paired with deep breathing, improves mood, focus and reduces stress which in turn helps reduce inflammation. Yoga
not exactly your thing? No worries; you can still experience the stress-reducing benefits by breathing deeply while you do nearly anything!Sitting Exercises
For anyone with limited mobility, sitting (or chair) exercises are a must! Chair exercises can build muscle, improve flexibility, increase circulation and keep your joints lubricated. Movement can include calf raises, seated marching, seated shoulder presses with weights or resistance bands, and sit-stands.
-
Can Supplements Really Reduce Your Inflammation?
The short answer: yes and no. To understand this answer, you first need to know the basics of inflammation and what to really expect from dietary supplements.
What is inflammation?
Before you start working to reduce inflammation levels, you should be familiar with the different types of inflammation and their effects on your body.
Simply put, inflammation is your body’s normal and essential response to any harmful or dangerous stimuli. You need inflammation to survive and thrive! Without inflammation how would your body react to a bee sting or other injury? Those are examples of acute inflammation which is characterized by pain, redness, heat, swelling and possibly loss of function or mobility.
Chronic and systemic inflammation is a little more elusive. People may have low-grade inflammation throughout their bodies and not know it for years. This can be dangerous because low-grade chronic inflammation has been linked to heart disease, type 2 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and obesity and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease. Symptoms of chronic inflammation are easily overlooked or written off as something else. Possible symptoms can include fatigue, fever, rashes or chest and abdominal pain.
Determining Your Risk
Chronic inflammation develops over time and can easily go unnoticed. However, certain risk factors can promote chronic inflammation that you should be aware of. These include age, obesity, diet, tobacco use, hormonal imbalances
and stress levels. In addition, if you are regularly exposed to toxins or irritants, have an autoimmune disorder or untreated acute inflammation you may also experience chronic inflammation. If you suspect that you might have chronic inflammation, visit your physician and request to have your [TVBLOGCOPY]C-reactive protein (CRP) [/TVBLOGCOPY][MWSBLOGCOPY]C-reactive protein (CRP)[/MWSBLOGCOPY] levels checked.If you find that your CRP is elevated or just want to improve your health, there are so many ways you can support your body to perform optimally.

Taking Control of Your Lifestyle
There’s no magic pill or potion for a poor lifestyle. Being genuinely healthy and experiencing wellness requires commitment and adequate time to allow your body to heal. Certain nutrients have been shown to help support healthy inflammation, but they can’t wholly overhaul years of processed foods, sedentary lifestyle and stress on their own.
Supporting a [TVBLOGCOPY]healthy inflammation[/TVBLOGCOPY][MWSBLOGCOPY]healthy inflammation[/MWSBLOGCOPY] response involves every aspect of your lifestyle. Supplements are intended to be used in conjunction with a healthy lifestyle. This involves eating a healthy [TVBLOGCOPY]anti-inflammatory diet[/TVBLOGCOPY][MWSBLOGCOPY]anti-inflammatory diet[/MWSBLOGCOPY], [TVBLOGCOPY]exercising regularly[/TVBLOGCOPY][MWSBLOGCOPY]exercising regularly[/MWSBLOGCOPY], drinking plenty of water, reducing stress and improving your [TVBLOGCOPY]mindset and attitude[/TVBLOGCOPY][MWSBLOGCOPY]mindset and attitude[/MWSBLOGCOPY].
-

5 Ways to Fight Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation is essential to your body’s natural healing process. However, when low-grade inflammation is unmanaged, it can become a serious issue. Unchecked inflammation isn’t always easy to detect. Likewise, it’s difficult to determine what is causing the inflammation. However, lifestyle choices play a significant role in inflammation levels which is why we’ve put together five tips to help you clean up your lifestyle and support healthy inflammation.
Step Away From Sugar
Regularly consuming sugary foods and drinks is linked to chronic inflammation, diabetes, cardiovascular disease and more. Sugar and artificial sweeteners go by many different names, some you may not easily recognize, which is why it’s more important than ever to read labels! But the best way to dramatically reduce your sugar intake is to avoid eating processed and pre-packaged foods.
to chronic inflammation, diabetes, cardiovascular disease and more. Sugar and artificial sweeteners go by many different names, some you may not easily recognize, which is why it’s more important than ever to read labels! But the best way to dramatically reduce your sugar intake is to avoid eating processed and pre-packaged foods.
Fill Up on Good Stuff
If you’ve been living off convenience foods and takeout you are setting the stage for chronic inflammation. But knowing which diet is best isn’t as simple as it should be. The most straightforward answer to “what should I eat” is found in the perimeter of the grocery store. Stick to fresh fruits, vegetables, wild-caught cold water fish like salmon and cod, whole grains and healthy fats. Limit nutrient-deficient foods like refined grains, fried foods and anything with artificial food additives.

Drink Up!
If you wait until you’re thirsty to drink water, you’re probably already experiencing some amount dehydration. Approximately 50-60% of your body is made up of water so even mild dehydration can have a profound impact on your health if you are chronically dehydrated. Aim to drink at least one liter of pure water every day. If you drink coffee, soda or alcohol, be extra mindful of your intake as these beverages can cause even more fluid loss.
Move Your Body
Sitting for long periods can take a toll on your health – even if you are an otherwise active person. The longer you stay in a fixed position, the more likely you are to experience muscle fatigue and aches due to the decreased blood supply to your muscles. Inactivity or a sedentary lifestyle is also linked to poor heart health, increased inflammation, excess weight and decreased immune function. If you work at a desk or otherwise find yourself sitting for long stretches throughout the day, break it up by performing stretches, going on a short walk or performing simple bodyweight exercises to get your blood flowing.
Find Time to Unwind
Unmanaged or chronic stress can throw your entire body out of whack. Prolonged physical, mental or emotional stress can alter your body’s ability to regulate stress hormones like cortisol which plays a role in immune and inflammation responses. To help avoid excess stress, make time for self-care and relaxation. This doesn’t mean sitting in front of the TV or computer screen; instead, go for a walk in nature, practice deep breathing or just sit in silence. Find whatever activity completely relaxes you and do it daily!
-

Inflammation Quiz — Is Your Lifestyle Hurting Your Health?
Acute inflammation is an essential part of the body’s healing process. Inflammation occurs at the cellular level when the immune system tries to fight off disease-causing germs or debris from an injury and repair damaged tissue. Once the fight is over the inflammation-triggering substances are supposed to retreat. However, when they don’t, it destroys the balance within your body and can make you more susceptible to premature aging and disease. Answer “yes” or “no” to the questions below to find out if any of your everyday lifestyle habits are contributing to chronic, unmanaged inflammation.
Answer “yes” or “no” to the questions below to find out if any of your everyday lifestyle habits are contributing to chronic, unmanaged inflammation.- Do you regularly eat processed foods, refined sugars or refined grains?
- On a typical day do you eat white bread, pastries, French fries, margarine, soda or other sugar-sweetened drinks?
- Do your meals rarely consist of whole, unprocessed fruits, and vegetables?
- Do you get less than 8 hours of uninterrupted sleep per night?
- Are you a smoker or routinely exposed to secondhand smoke?
- Are you overweight or obese?
- Do you routinely drink less than one liter of pure water per day?
- Do you feel anxious, hopeless or stressed out most of the time?
- Is your exercise unbalanced? For example, do you live a sedentary lifestyle or routinely overtrain?
- Do you sit for long stretches of time at work or home?
-
The Importance of C-Reactive Protein
We have been saying this for nearly a decade — Your C-Reactive Protein (CRP) inflammatory marker DOES matter!
In fact, according to Harvard Medical researcher Dr. Paul Ridker principle investigator on many CRP clinical studies, it matters more as an indicator of your heart and cardiovascular health than your cholesterol readings! This may not be a popular opinion today, but it is a scientifically researched opinion.
Please read the full article from Harvard Medical. This may surprise and even shock you!
There is still good news for you if your marker was high. Through smart choices and a few simple steps, you can improve your CRP and significantly enhance your cardiovascular health.
Step 1
- Eat a low-inflammatory food diet. Get the Inflammation Food Pyramid from TriVita
Step 2
- Add physical activity to your day, just walking 30 minutes a day can make a difference
Step 3
- Include [TVBLOGCOPY]Nopalea[/TVBLOGCOPY][MWSBLOGCOPY]Nopalea[/MWSBLOGCOPY] in your daily nutrient intake
- Managing your inflammation is one of the most important things you can do for your heart and brain health!
- Life is wonderful and beautiful when living with greater wellness!
-

Three Easy Ways to Reduce Inflammation with Exercise
When it comes to managing inflammation, there isn’t one thing that will work. Instead, it’s essential to turn your focus to every aspect of your lifestyle. Eat a healthy diet full of anti-inflammatory foods, reduce stress, supplement wisely and choose the right types of exercise. One study followed over 4,000 middle-aged men and women for 10 years and found that individuals that met the national physical activity guidelines were able to lower their inflammation by 12 percent. Just 20 minutes a day is enough to reduce inflammation, but what are the best activities when recovering?Walking
Whether you feel achy, lack the motivation to hit the gym or just need to reset your body, walking is an excellent choice. Going for a long walk is a great way to reap the benefits of daily activity without increasing inflammation. Even just a walk around a park or through your neighborhood is enough to get your heart pumping, moving fresh blood and oxygen to muscles and boost your mood.Swimming
Swimming is a fantastic option for anyone looking for a low-impact workout. It offers all the benefits of other aerobic exercises without damaging your joints. In addition to the cardiovascular benefits, swimming can help improve muscle strength and flexibility.
A study published in Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity found that just 12 weeks of yoga practice and meditation resulted in lower levels of inflammation and significantly lower levels of cortisol. Deep, controlled breathing associated with both yoga and meditation help to calm the nervous system and promote physical and mental relaxation which is important when dealing with unmanaged inflammation. Yoga and Meditation
Yoga and Meditation -
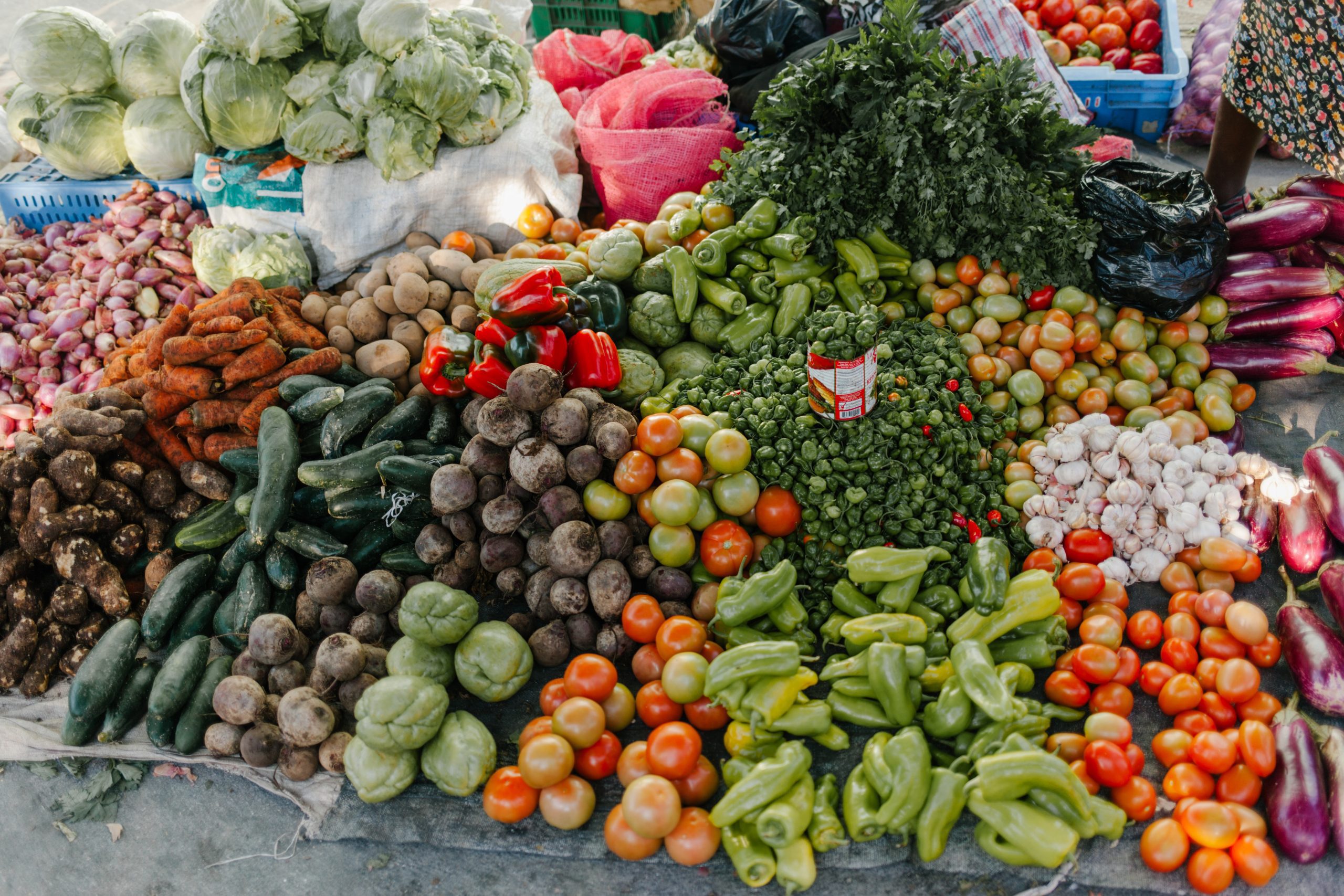

The Inflammation Food Pyramid
How do the pieces of an anti-inflammatory diet fit together? This pyramid shows the general guidelines. The base is the foods you should eat the most of; moving up, you see the foods and nutrients you should eat in smaller quantities, or less often.
Nutritional supplements
A good quality multi-vitamin will help fill in nutritional gaps; a multi-strain probiotic taken before bed will ensure good digestive and immune health; and fish oil helps make certain we get enough omega-3 essential fatty acids.Hydration
Drinking enough water is the single best way to improve the way we feel and look. Try for about 34 ounces daily for every 50 pounds of body weight.Herbs & spices
Want to speed up metabolism, reduce inflammation and reap even more benefits? Keep your home stocked with ginger, garlic, parsley, oregano, cilantro, basil, turmeric, nutmeg, cinnamon and cayenne pepper.Fruit
Two servings per day maximum for an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, because many fruits are high in sugar. Green apples and berries are the lowest-sugar fruits.Complex carbohydrates
These have enough fiber to slow the release of glucose (sugar) into the system, helping to stabilize blood glucose levels. Stable blood sugar levels are the ONE thing that people who live to be 100 or over have in common.- Grains: Choose gluten-free grains whenever possible, like brown and wild rice and quinoa.
- Root veggies: Sweet potatoes, yams, butternut and acorn squash and parsnips.
- Beans & legumes: Chickpeas, black beans, pinto and adzuki beans, lentils.
Healthy fats & oils
Good-quality fat makes us feel full, so we won’t overeat sugar or carbohydrates, and are a fast way to strengthen the immune system and reduce inflammation.Protein
Consuming high-quality meats (free-range and organic lean meats and wild fish) provides the body with sources of complete protein and all the essential amino acids necessary to repair tissue and maintain a healthy metabolism.Vegetables
It’s simple—the more fresh vegetables we eat, the better our health will be. A rainbow of color and five servings per day keep antioxidant levels high and inflammation at bay. You can download a PDF version of this article here. -

At the “Heart” of Good Health: Omega-3 Fatty Acids
By Samuel Grief, M.D. Scientists often discover health breakthroughs by good luck and circumstance. In the 1960s a researcher studied why Canada’s northern Eskimos weren’t suffering from heart disease as much as other North Americans, even though the Eskimos were eating a diet very high in fat (seal and polar bear flesh). It turned out that the flesh of these animals, and certain northern fish, was rich in a type of fat known as omega-3. Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fatty acids. But omega-3s are unique in adjusting cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood in a way that benefits our heart and arteries. Further research has clarified the now-accepted fact that omega-3 fatty acids do not clog our arteries. More importantly, omega-3s actually help thin the blood and lower levels of circulating fatty acids in the blood. These last two effects are probably why the Eskimos staved off widespread heart disease.Prescribed to lower disease risk
Omega-3s are now prescribed by physicians to help lower the risk of heart disease. In fact, the American Heart Association and other medical authorities in the U.S. and around the world also recommend a diet rich in omega-3s and taking a supplement in varying doses, depending on your health status and medical conditions. Omega-3s have been studied for many other medical conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes and abnormal heart rhythms. Science confirms that there is indeed a positive impact on these conditions when taking anywhere from 2,000–4,000 milligrams of omega-3s daily. Omega-3s are now incorporated into infant formulas as a way of enhancing brain development. After all, the brain is 60% fat—what better way to nourish a growing child’s brain than by giving that child a healthy form of fat? You can get your omega-3 supply from fatty fish—typically salmon, tuna, halibut, sea bass and some predatory fish like king mackerel, swordfish and others. Be careful not to overeat the large, predatory fatty fish as they also contain more potentially harmful heavy metals such as mercury. Some plant foods contain the precursor to omega-3s, known as Alpha Linolenic Acid (ALA). ALA is found in walnuts, tofu and many seeds. For good health, eat a healthy and balanced diet, and get your daily dose of omega-3 fatty acids. This article is intended for educational purposes only. Graphic used with permission from GOED, the Global Organization for EPA and DHA Omega-3s.
Graphic used with permission from GOED, the Global Organization for EPA and DHA Omega-3s.
References: Omega-3 fatty acids, fish oil, alpha-linolenic evidence. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved from http://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/omega-3-fatty-acids-fish-oil-alpha-linolenic-acid/evidence/hrb-20059372. Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS, Apple LJ. American Heart Association Nutrition Committee. Fish Consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. 2002. Circulation. 106:2747-2757. National Institutes of Health. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program Expert panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). 2001. NIH Publication Number 01-3670. Washington, DC. [online] Retrieved from http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/cholesterol/atp3full.pdf. Vannice G and Rasmussen H (2014). Position of the academy of nutrition and dietetics: dietary Fatty acids for healthy adults. J Acad Nutr Diet 2014. 114:136-153. [online] Retrieved from http://download.journals.elsevierhealth.com/pdfs/journals/2212-2672/PIIS2212267213016729.pdf. -
The Connection Between C-Reactive Protein, Inflammation and Heart Disease
Why you should ask your doctor for a CRP test
By Lester Adler, M.D., M.D.H. For all the ways bodies are harmed, by viruses, bacteria or trauma, the immune system has but one defense: inflammation. Just a hard pinch will initiate swelling, redness, heat and pain. Specialized cells rush to the call ready to engulf invaders, while others break down compromised tissue so yet others can rebuild, leaving it good as new. Sounds perfect, doesn’t it? Yet many diseases result from the immune system in overdrive. Take heart disease—what was once blamed on dietary fat is now understood to be also about inflammation. Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) starts with a streaky deposit of cholesterol in an artery. The immune cells infiltrate the area to get rid of it, but instead attract more cholesterol, adding to the growth of the plaque. Eventually, complete closure or catastrophic loosening of the clot into the bloodstream could cause a heart attack or stroke. Since this all unfolds below the surface, doctors use diagnostic markers to reveal this disease before it’s too late. Heart disease risk C-reactive protein is one of the hundreds of molecules used in the immune process. Produced by the liver in response to infection or inflammation, and also secreted by fat cells, CRP usually spikes within 48 hours of an acute insult after which it dissipates. But in chronic inflammation, it remains elevated. For instance, people with gum disease have unresolved infection, inflammation, higher CRP levels and higher risk for heart disease. Heart disease was rare just 100 years ago. Therefore this is an elective disease caused by our own lifestyles. Decreasing CRP could be one of the best ways to keep your immune system from turning against you. Essential CRP testing Knowledge is power. This is all the more true when it comes to our health. Since many diseases result from our own lifestyle choices, proper information can motivate us to make a major directional turn. One of the miracles of modern science is the serum blood test. Hundreds of molecules travel through our bloodstream, each one telling a story about our health. When you get your annual blood test, your doctor looks for important indicators that, if out of range, guide in treatment. C-reactive protein (CRP) is not typically among them. Don’t let that stop you. C-reactive protein is an established marker for inflammation, the defense and repair process of the body. It is designed for acute situations. When the irritant, and therefore, the inflammation doesn’t resolve, it hurts cell membranes, such as in arteries and veins. Elevated CRP is linked to a three-fold increase in heart attacks. But, heart disease is just one reason to have your CRP tested. Cancer, chronic lower respiratory disease, stroke, dementia, diabetes and nephritis are also attributed to chronic inflammation. Even depression is now recognized as an inflammatory process. These diseases are usually long in the works. Inflammation silently irritates or “burns” tissue on a microscopic level. At some point symptoms break through. One day a person has a hard time walking. One day they realize that their cough isn’t going away. Or, one day they have a major event like a heart attack or stroke.
The good news is that inflammation and CRP can be brought down. Proper diet, exercise, stress reduction and supplementation can ease the fire allowing tissues to recover… the sooner, the better.
If you would like your doctor to order you a CRP test, ask for one. Say that you have learned that chronic inflammation is a silent condition and you would like to know if you have it. If your insurance will not cover it, then find out what the cash fee is and pay in advance. It could be as little as $10–$20.
I suggest requesting an hs-CRP (high sensitive) test from your doctor. The optimal range is under 0.55 mg/L in men and under 1.5 mg/L in women. 2.4 mg/L has been associated with a doubled risk of a coronary event compared to levels below 1 mg/L; over 11 indicate acute inflammation.
Remember, the CRP test is well worth the investment in your future health.
This article is intended for educational purposes only.
These diseases are usually long in the works. Inflammation silently irritates or “burns” tissue on a microscopic level. At some point symptoms break through. One day a person has a hard time walking. One day they realize that their cough isn’t going away. Or, one day they have a major event like a heart attack or stroke.
The good news is that inflammation and CRP can be brought down. Proper diet, exercise, stress reduction and supplementation can ease the fire allowing tissues to recover… the sooner, the better.
If you would like your doctor to order you a CRP test, ask for one. Say that you have learned that chronic inflammation is a silent condition and you would like to know if you have it. If your insurance will not cover it, then find out what the cash fee is and pay in advance. It could be as little as $10–$20.
I suggest requesting an hs-CRP (high sensitive) test from your doctor. The optimal range is under 0.55 mg/L in men and under 1.5 mg/L in women. 2.4 mg/L has been associated with a doubled risk of a coronary event compared to levels below 1 mg/L; over 11 indicate acute inflammation.
Remember, the CRP test is well worth the investment in your future health.
This article is intended for educational purposes only.
-

Muscle Loss Linked to Chronic Inflammation
Many physiological changes occur with aging, and recent research shows that sarcopenia and loss of overall muscle strength can be added to the list of health concerns associated with unaddressed inflammation. Recent research shows that age-related chronic low-grade inflammation is a contributing factor to sarcopenia and affects both the breakdown and synthesis of muscle. Older people who suffer from sarcopenia are more likely to have high blood levels of the inflammatory markers such as CRP, SED rate and adipoenctin.What is Sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia is the age-related loss of muscle mass, strength and function that generally appears after the age of 40 and accelerates after the age of 75. It is estimated that between 25 and 50 percent of North Americans over the age of 65 suffer from sarcopenia that is significant enough to limit their daily activities. Age-related loss of muscle strength robs older adults of their independence and heightens their risk of experiencing devastating injuries and possibly death from sudden falls and other accidents. While mostly observed in physically inactive adults, sarcopenia is also seen in older adults that remain physically active throughout their lives. Regularly engaging in physical activity is essential to avoiding sarcopenia, but inactivity isn’t the only contributing factor. Sarcopenia is a multifaceted disease that may result due to inflammation, nutritional imbalances and lack of resistance training, neurological decline and mitochondrial decline.Prevent and Slow Muscle Loss
Scientists are working to understand the causes of sarcopenia; however, most interventions have focused on improving muscle strength and nutrition. Exercise provides some stimulus and benefits, but during times of bed rest, such as after surgery or injury, mobility may be severely limited. One study set out to determine if supplementation with essential amino acids (EAA) could offset muscle loss experienced during prolonged inactivity. During the 28-day trial, researchers observed lean leg mass was maintained in the experimental group. The group also retained more muscle strength than the control group. Researchers determined, “supplementation may represent a viable intervention for individuals at risk of sarcopenia due to immobility or prolonged bed rest.” Your lifestyle plays a significant role in building strong muscle as you age. Many people assume they can add more protein to their diets to make up for lost muscle mass, but that may not be enough. The role of protein in food is not to provide our bodies with proteins directly, but to supply the amino acids from which the body can make its own proteins. When we eat foods that supply each essential amino acid in adequate amounts, our body supports protein synthesis.Check Your Inflammation
Inflammation is the immune system’s response to damage and helps fight infection and heal injuries. However, inflammation, like stress, is meant to be an acute process in the body, designed to serve a purpose, then resolve. When it becomes chronic, it depletes the body’s resources and causes deep damage to tissues and organ systems. A simple blood test is used to measure C – reactive protein (CRP) in the body. The CRP test isn’t site-specific, so it shows the overall level of inflammation and a low level of CRP doesn’t necessarily mean there is no inflammation present.
There are simple steps you can take to help support healthy inflammation. Aim to avoid pro-inflammatory foods and choose high-quality vegetables rich in antioxidants, healthy fats and drink enough water. Other healthy lifestyle choices include managing stress and maintaining healthy body weight.
A simple blood test is used to measure C – reactive protein (CRP) in the body. The CRP test isn’t site-specific, so it shows the overall level of inflammation and a low level of CRP doesn’t necessarily mean there is no inflammation present.
There are simple steps you can take to help support healthy inflammation. Aim to avoid pro-inflammatory foods and choose high-quality vegetables rich in antioxidants, healthy fats and drink enough water. Other healthy lifestyle choices include managing stress and maintaining healthy body weight.
Use It or Lose It
Adopting a regular exercise program is another way to slow down the loss of strength and coordination. Any type of exercise is better than none; however, resistance training (using weights, machines or bands) is critical for those looking to preserve or increase muscle strength and mass. Regular exercise that includes strength training promotes mobility, overall fitness and improves bone health as well. New research published in the journal Brain, Behavior and Immunity, reported that a 20-minute session of moderate exercise could have anti-inflammatory effects. Suzi Hong, Ph.D., one of the studies researchers says, “Our study found one session of about twenty minutes of moderate exercise resulted in a 5 percent decrease in the number of stimulated immune cells producing TNF.” The primary role of TNF, which is a type of protein that is involved in systemic inflammation, is to regulate immune cells. By adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes balanced dietary modifications, nutritional supplements and regular physical exercise, it is possible to support healthy inflammation response in the body and preserve muscle strength at any age! -

4 Ways to Ease Inflammation (That You’ve Probably Never Heard Of!)
Inflammation is a hot topic, and for good reason! An inflamed body can show up as so many health conditions: an achy body, weight gain, low energy and even aging faster!1
Here are 4 sneaky ways that you can help to ease and even prevent inflammation:Ban Electronics From The Bedroom
Gadgets are a part of everyday life, and we can’t live without them. But if you bring them into your bedroom, this is an open invitation to bring inflammation into your life. The light from the screen of a TV or smartphone can throw off your body’s internal clock. This makes getting a good night’s sleep next to impossible. Even if the screens are turned off, the tiny blinking notification or power lights can be sensed by the photoreceptors in your skin!2 Poor sleep leads to an increase in inflammation.3No Sweetened Beverages
Stay away from sweetened drinks! It doesn’t matter if it’s diet or regular. People who drink beverages that are sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup or artificial sweeteners often have higher levels of insulin in the body4. Therefore, this can cause more inflammation.5Avoid AnyY Artificially Colored Foods Or Drinks
Check your food labels for any ingredients that you can’t pronounce—they’re usually full of inflammatory substances. Also, avoid any artificially colored foods and drinks. Unless they contain blueberries, a bright blue food isn’t likely to do anything good for your immune system! A weak immune system is associated with higher levels of inflammation in the body.6Drink Green Tea
Green tea has natural ingredients called polyphenols. They help the body detoxify and also fight free radicals which are a cause of inflammation in the body7. Try to drink 1 -3 cups of green tea daily!
Sources:- http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1196/annals.1322.001/full
- https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article-lookup/doi/10.1210/jc.2004-0957#61568045
- https://academic.oup.com/sleep/article/32/2/200/3741730/Sleep-Duration-and-Biomarkers-of-Inflammation#main
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/is-fructose-bad-for-you-201104262425
- http://www.todaysdietitian.com/newarchives/020314p44.shtml
- http://www.todaysdietitian.com/newarchives/020314p44.shtml
- http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/ben/chddt/2007/00000007/00000002/art00008
-

The Benefits of Fish Oil
How adding fish oil to your diet can help
All saturated and monosaturated fats can be made by the body and do not need to be supplied through the diet. However, the body is unable to make two types of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) that have been shown to have much beneficial health effects1:- Alpha-linolenic acid (Omega-3) found in flaxseed, flax oil, spinach, broccoli
- Linoleic acid (Omega-6) found in soy oil, sesame seeds, corn oil, and most nuts
Brain and Nerve Health Support2,3
- Approximately two-thirds of the human brain is made of fat
- Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA are among the most important brain health nutrients
- DHA is the primary structural component of the brain
- Omega-3 and Omega-6 PUFAs constitute 30-35% of total brain fatty acids
- DHA levels decrease with age and are affected by the number of fatty acids in the diet
Vision Support4,5
- DHA is also critical for the development and function of the retina
Healthy Heart5,6
Omega-3 EPA/DHA:- May decrease triglyceride levels in plasma as well as the level of total and LDL (bad) cholesterol
- May normalize blood pressure by helping to increase and decrease levels of compounds that may result in blood vessel relaxation
Are Americans meeting nutritional guidelines for Omega-3 fatty acids? 7
- The 2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend consuming 250 mg/day of Omega-3 fatty acids (two 4 oz. servings of seafood/week)
Premium Fish Oil in an Easy-to-Swallow Soft Gel
If you’re considering adding Omega-3 to your diet, consider Omega3Prime supplements from TriVita, one of the cleanest, purest, and traceable fish oils on the market.
Sources:- http://web.stanford.edu/group/hopes/cgi-bin/hopes_test/fatty-acids/#saturated-vs-unsaturated-fat
- Luchtman DW, et al. Neuropharmacology 2013;64:550-565
- http://www.nutrasource.ca/uploads/userfiles/images/omega-3s%20and%20the%20brain%20-resized-600.png
- Innis SM. J Nutr 2007;137(4);855-859; Deckelbaum RJ, et al. J Nutr 2012;587S-591S; Wiktorowska A, et al. Adv Clin Exp Med 2015;24(6):931-941
- Wiktorowska A, et al. Adv Clin Exp Med 2015;24(6):931-941
- Bradberry JC, et al. P&T 2013;38(11):681-691
- Papanikolaou Y, et al. Nutr J 2014;13:31